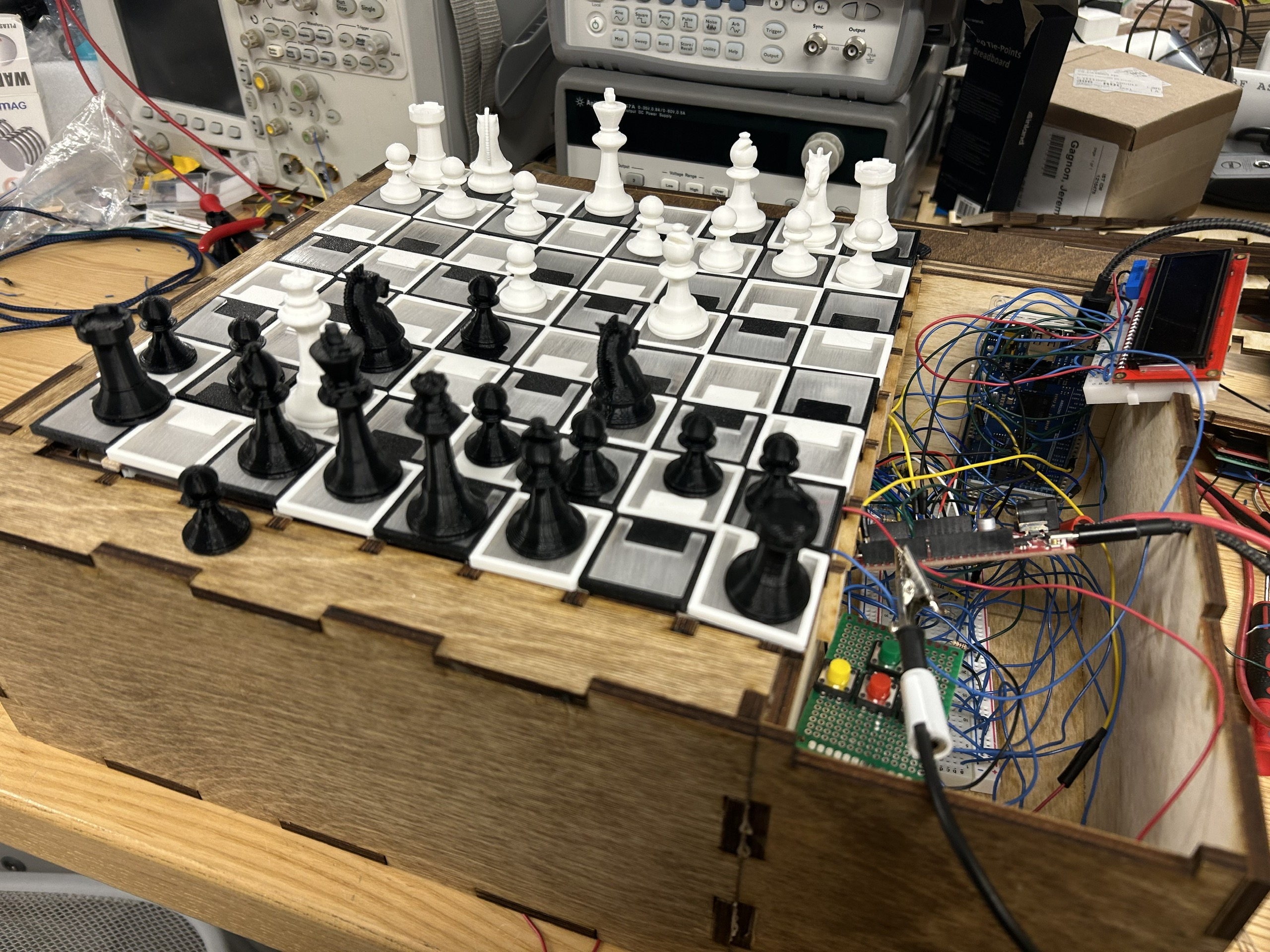
Overall Architecture
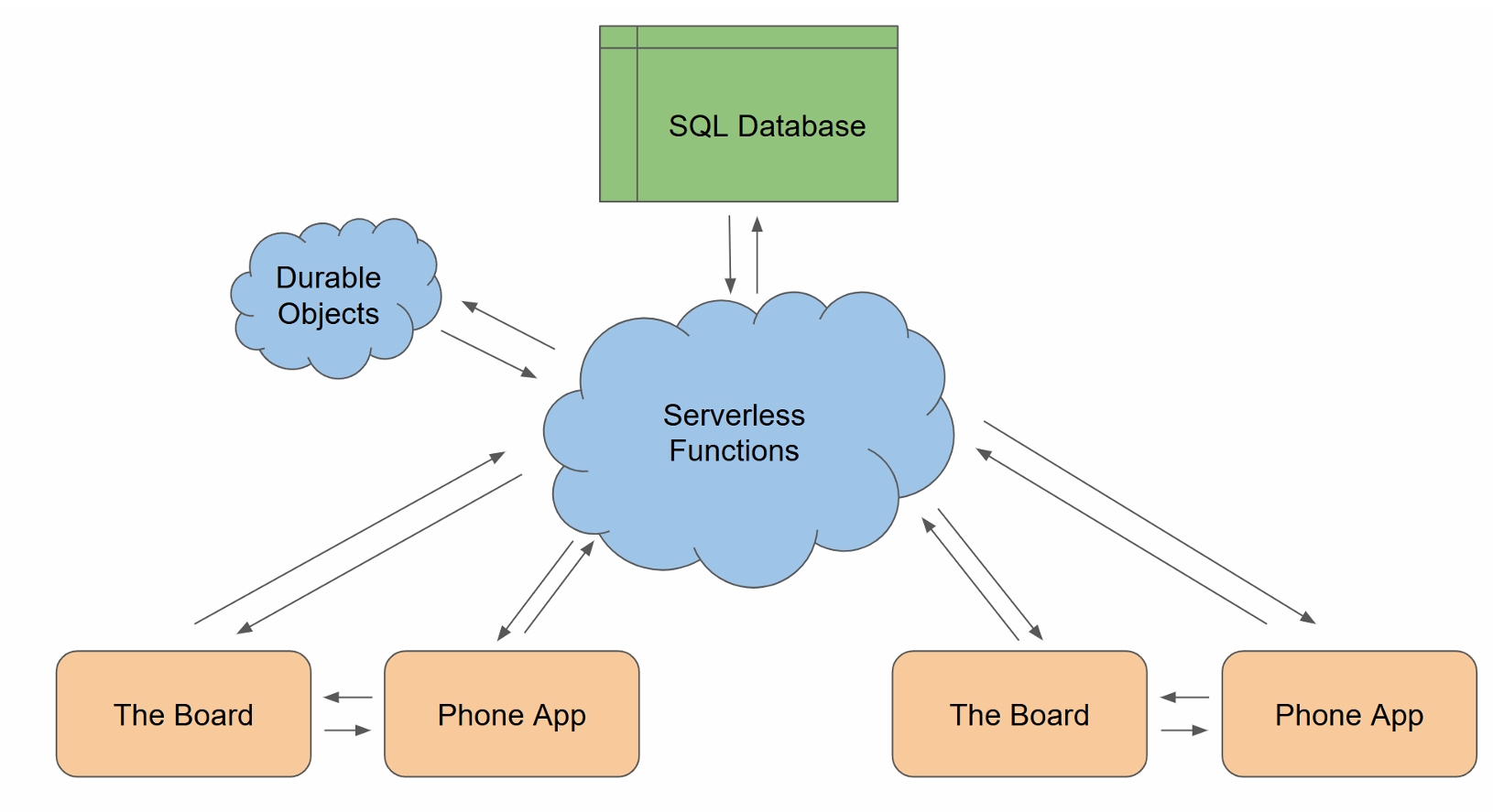
A depiction of the overall project communication flow
Frame Design
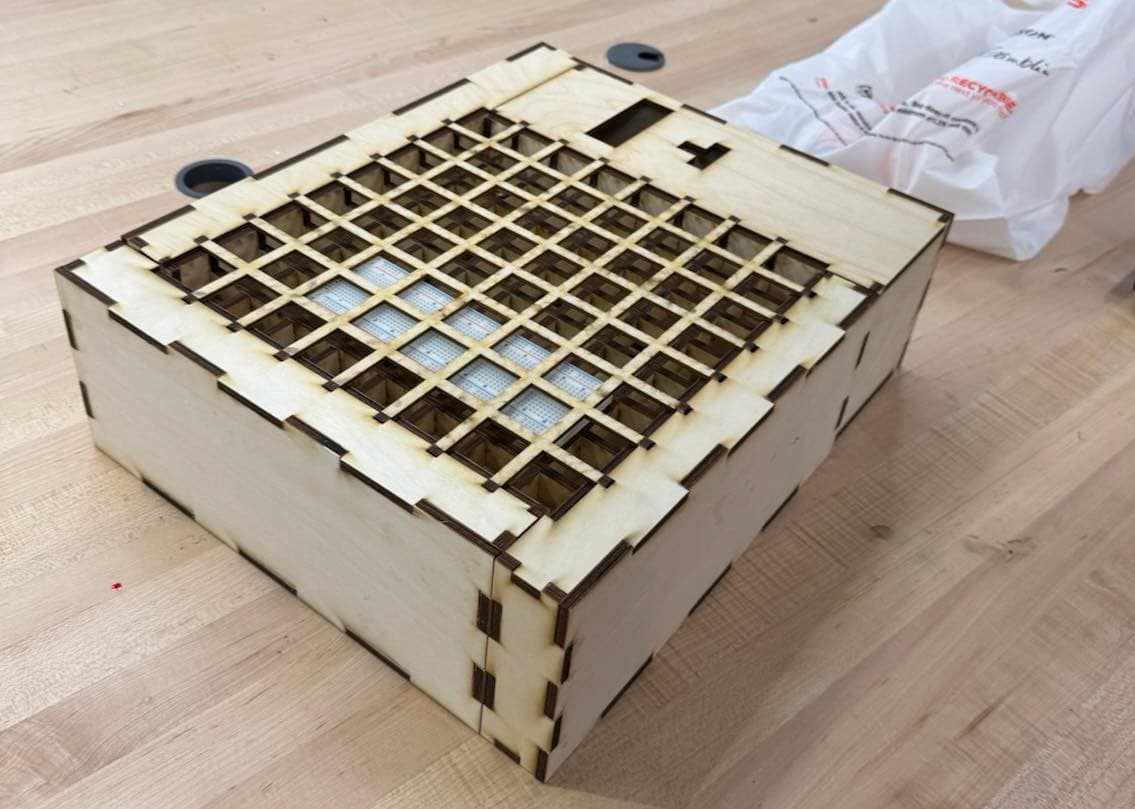
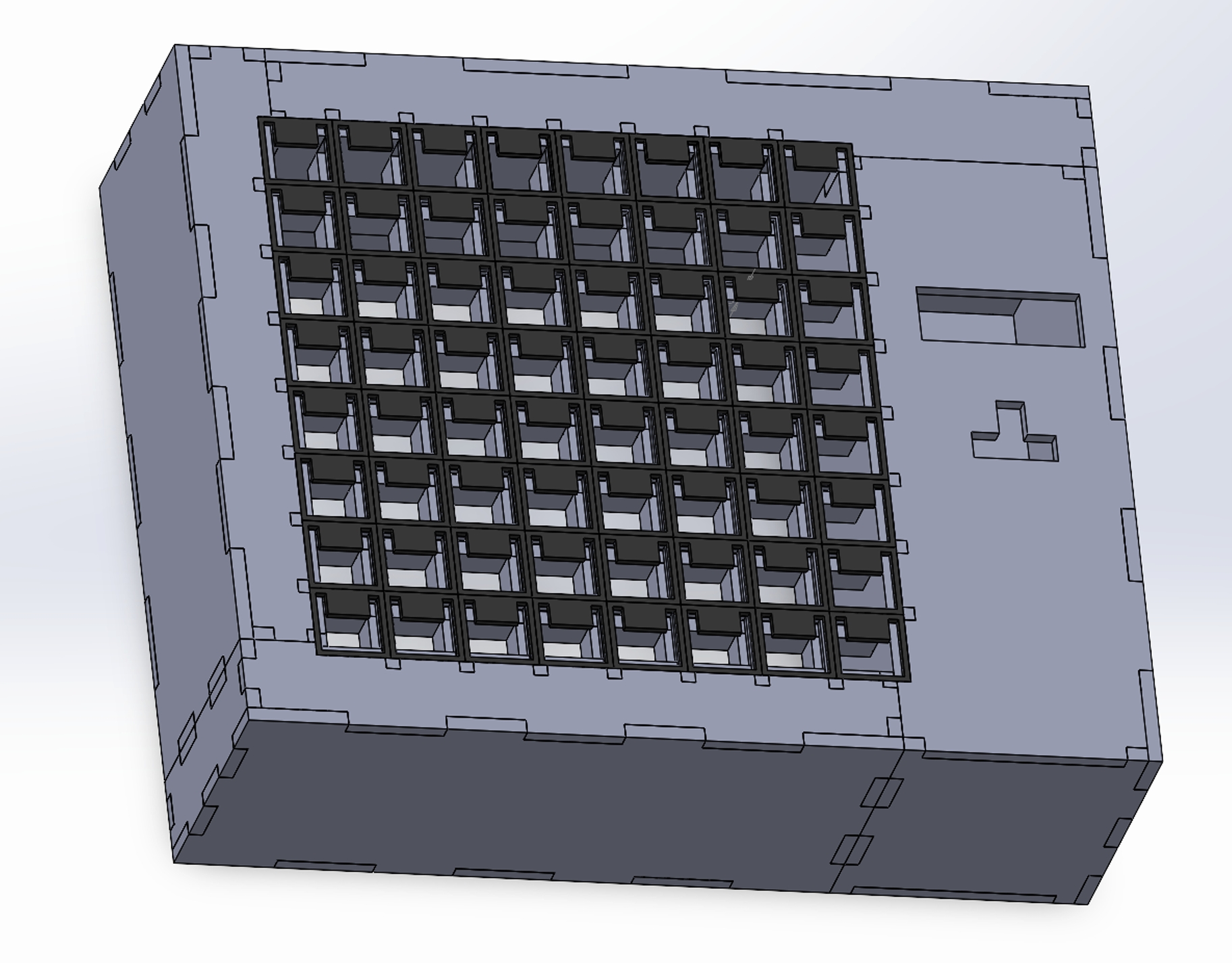

Frame Design
The mechanical part of the board consisted of the frame, the struts, the cover, and the squares.
The board was fully constructed from birch plywood due to it being very cost-effective and sturdy. The squares themselves were 3D printed with an acrylic insert. By making them out of more common materials, it is easy to customize the board by changing different parts to better fit what the user wants.
Circuit Design
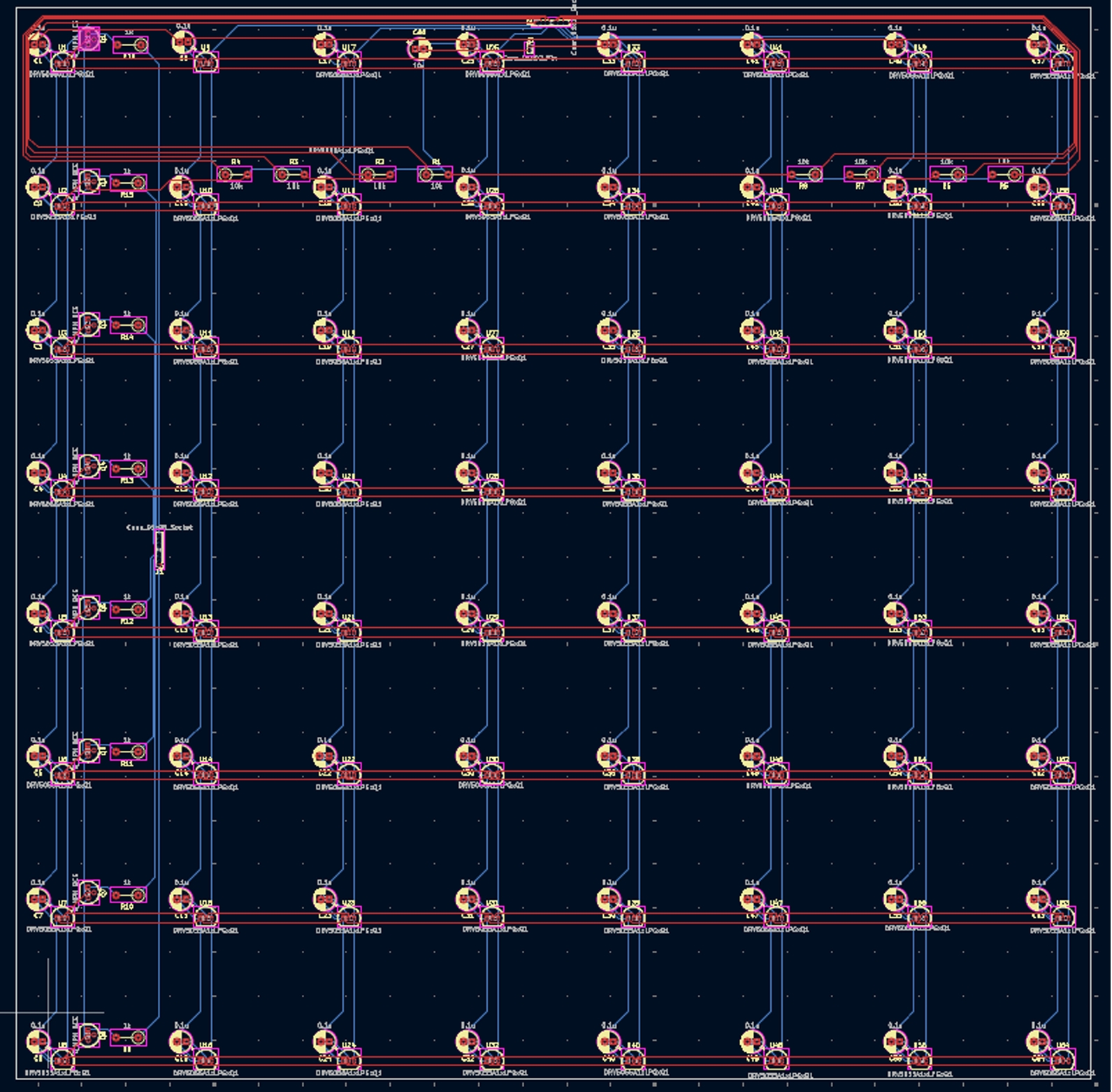
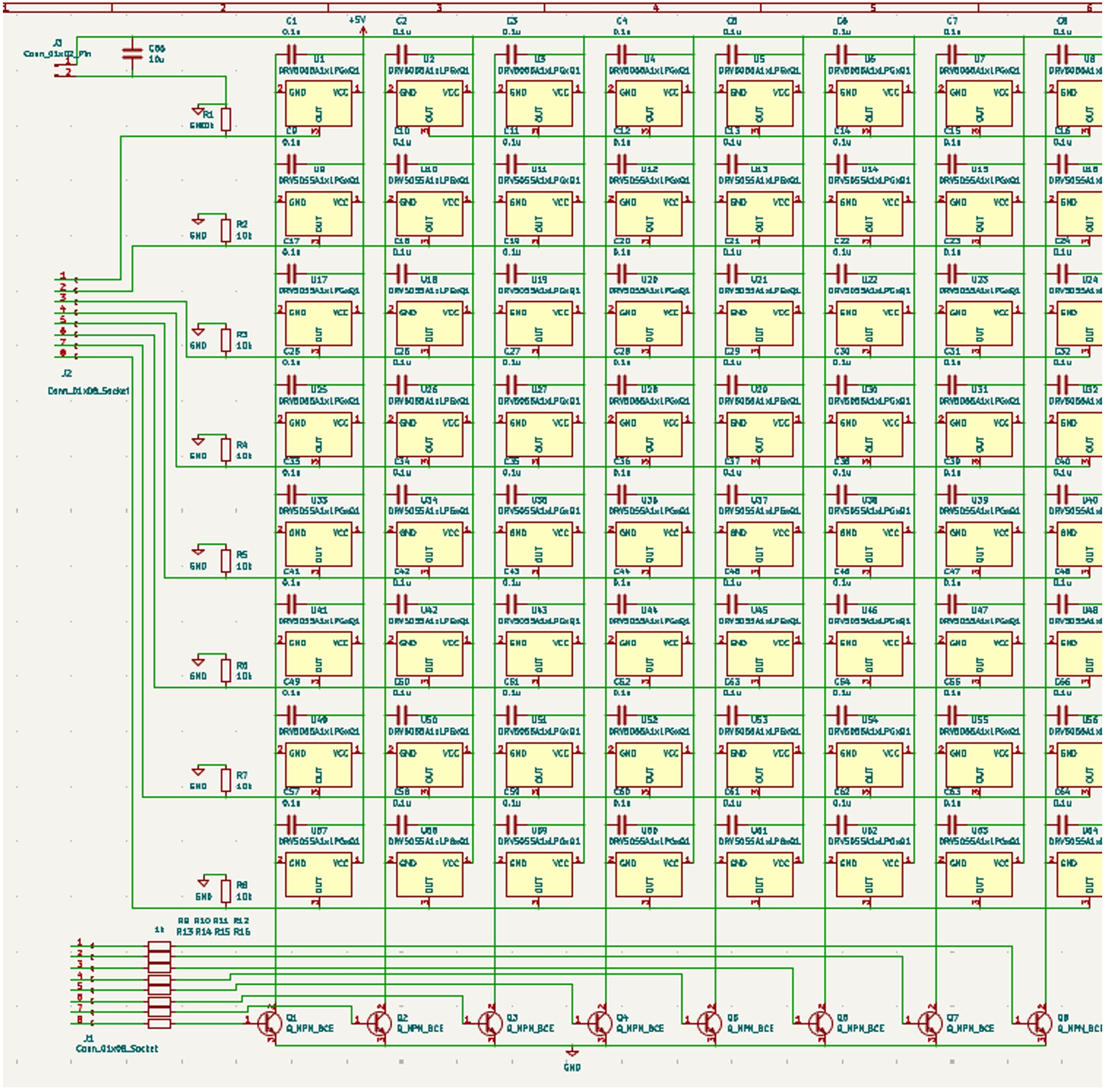

Circuit and PCB Design
The sensor system of the ChessLink board was designed using a switch matrix configuration, where Hall effect sensors were arranged in an 8×8 grid to detect piece positions. The VIN pins of the sensors were routed across rows, while the output signal pins ran down columns. Each sensor’s ground was controlled by 2N2222 transistors acting as row switches, which were driven by eight digital I/O pins from the Arduino Giga. Another eight analog inputs were used to read signals from each column. By sequentially activating one row at a time and reading the outputs from the columns, the board could detect magnetic piece placement. This method required a brief delay between row switching and signal reading, resulting in a full board scan time of approximately 200 milliseconds.
To indicate moves, each square was outfitted with two LEDs mounted on parallel-connected strips. To reduce computational demand on the Arduino Giga, these LEDs were controlled by a separate Arduino Uno, which received RGB commands and position data via a serial interface. Power was supplied by a Samsung 21700 USB-C rechargeable battery, enabling portable use. Because the system included both 3.3V and higher-voltage components, two boost converters were used to step up the voltage for powering 5V LEDs and 9V Arduino boards, with an overall efficiency of approximately 90%. This integrated system enabled responsive, untethered gameplay with both visual feedback and accurate piece detection.
Chess App
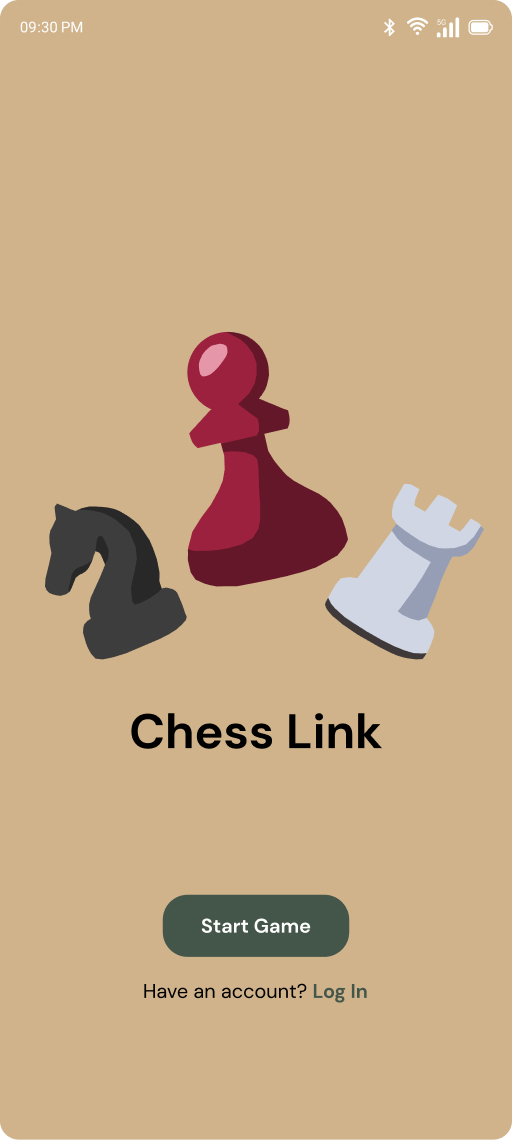




App Design
The Chess Link mobile application was developed using Flutter, chosen for its cross-platform compatibility and ease of integrating Bluetooth and network-based communication. The Chess Link app provides a full-featured user interface that enhances the gameplay experience beyond just board connectivity.
The app uses Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) to establish a direct connection with the smart chessboard. Once paired, the app sends control signals such as player moves, game initiation commands, and board reset instructions. It also receives updates from the board, such as confirmation of valid moves and illegal move alerts. The BLE communication is handled through Flutter plugins like flutter_blue_plus, which provides access to the Giga’s BLE services.
It communicates with the backend mostly through a combination of WebSocket
connections for real-time gameplay updates and HTTP API requests for actions like user
authentication, match creation, and statistics retrieval. The app listens for move updates and
game state changes through the WebSocket channel and reflects them both on the app’s interface
and the physical board.
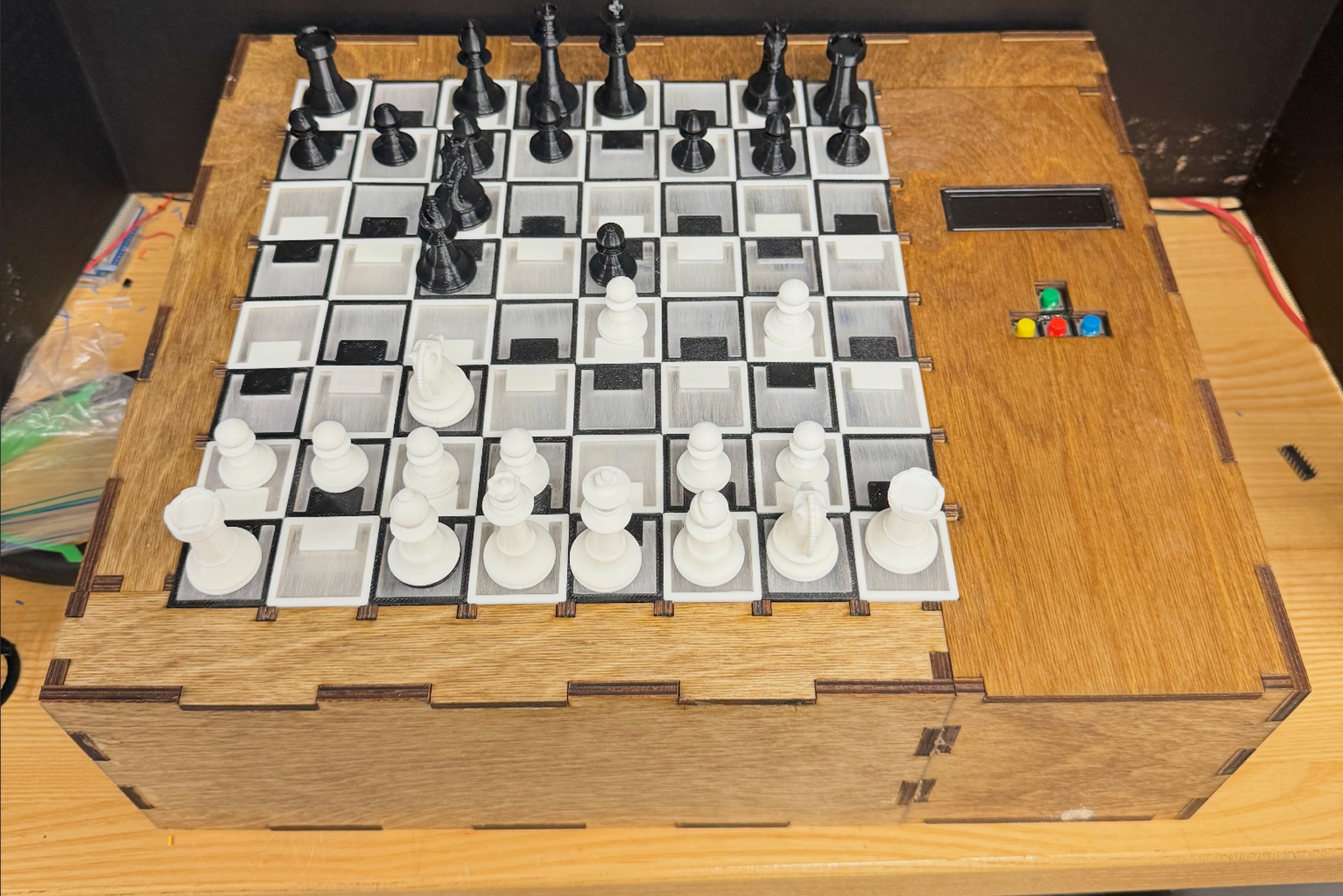
Demo
To demonstrate the capabilities of Chess Link, the board uses Hall effect sensors to detect the
presence and movement of chess pieces on a grid. Each sensor corresponds to a specific square,
allowing us to track piece positions in real time. When a piece is lifted and placed on another
square, the system detects the change in magnetic field and sends that data to an Arduino Giga
WiFi board, which communicates the move to an external app via WiFi.
Most importantly, the board introduces a novel communication feature: the ability to send messages to each other as well as emojis, which display on the physical board without disrupting gameplay. This makes the experience more immersive and personal than simply clicking on a screen, and enables long-distance play that feels face-to-face.
CHESSLINK

Github Link
https://github.com/ThTran13/ChessLink.git